An allylic hydrogen is a hydrogen atom that is bonded to an allylic carbon in an organic molecule.
Allylic and vinylic hydrogens.
Allylic vinylic examples organic chemistry duration.
In other words it is a methylene bridge ch 2 attached to a vinyl group ch ch 2.
Chlorination of allylic hydrogen is difficult than vinylic hydrogen.
A hydrogen atom bonded to an sp 2 carbon of an alkene.
When one hydrogen atom is removed from the third carbon atom of a propane molecule it is equivalent to an allyl group.
An allylic carbon is an sp3 carbon that is adjacent to a vinylic carbon.
Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule.
Atoms or groups attached to an allylic carbon are termed allylic substituents.
None of the other hydrogens are vinylic.
An allylic carbocation in which an allylic carbon bears the positive charge.
Allyl group holds three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms on the other hand vinyl group has two carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms.
Identify the number of allylic and vinylic hydrogens in the pictured molecules.
Br allyl radical is stabilished by resonance.
It contains two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and one sp 3 hybridized carbon atom.
Identify the number of allylic and vinylic hydrogens in the pictured molecules.
The libretexts libraries are powered by mindtouch and are supported by the department of education open textbook pilot project the uc davis office of the provost the uc davis library the california state university affordable learning solutions program and merlot.
Benzylic position allylic position propargylic position aryl aryl hydrogen.
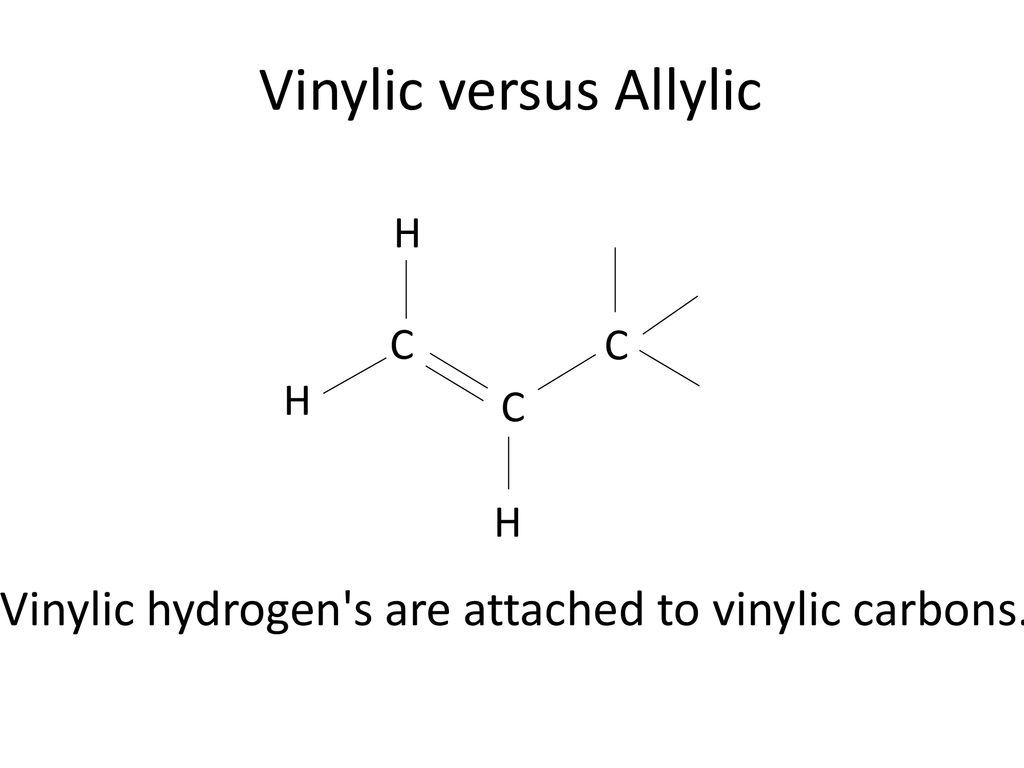
The vinylic hydrogens are shown in red.
Allyl form a stable carbocation because of the electron delocalization whereas vinylic carbocations are unstable as they lack p character.